Static Elimination in No-airflow Environments
Normally, static eliminators (ionizers) are used with blowers and air jets to increase static elimination efficiency. However, in cases where lightweight or tiny workpieces are involved, these methods cannot be used since the airflow can adversely impact the workpieces.
Static elimination with no airflow is required for such cases. Here, we explain the principle of eliminating static electricity in no-airflow environments without compromising static elimination performance and introduce case studies on this topic.
- What is static elimination in no-airflow environments?
- Principle of blowerless static elimination
- Example of eliminating static electricity using a blowerless ionizer
What is static elimination in no-airflow environments?
When sheets, films, or electronic parts are transported by a roller or a parts feeder, these workpieces become charged and collect foreign particles. Using a dust collector in such a process as a way to remove foreign particles can make sheets and films flutter with suction air or cause small, light electronic parts to be blown away. In addition, static eliminators (ionizers) are generally used with air jets to deliver the ions necessary for efficiently eliminating static from the target. However, it can be difficult to install systems like this due to the need for an air jet system.
Static elimination in no-airflow environments removes static charge from workpieces sensitive to dust, particles, or wind pressure while preventing adhesion of foreign particles.
Principle of blowerless static elimination
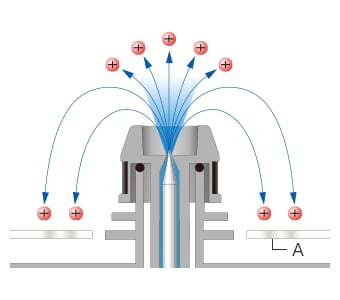
Some ions for static elimination generated by the static eliminator (ionizer) go to the exposed GND plates and do not reach the static elimination target, preventing sufficient static elimination.
To work around this problem, the GND plates are embedded in the static eliminator (ionizer). This allows the ions generated by the ionizer to reach the target with no loss and without going to the GND plates. Additionally, setting the ion generation cycle according to the distance to the target can prevent rebonding, which improves the efficiency of static elimination in a no-airflow environment.
In other words, embedding the GND plates inside the static eliminator and setting the ion generation cycle to an appropriate value can reliably eliminate static and prevent adhesion of foreign particles even in no-airflow environments.
- GND plates are exposed
-
- GND plates are not exposed
-
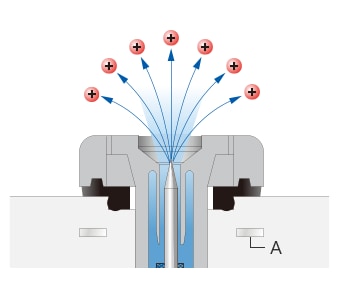
- A: GND plate
Example of eliminating static electricity using a blowerless ionizer
Non-blower type ionizers remove static charges from delicate parts that are sensitive to dust and wind pressure without using air.
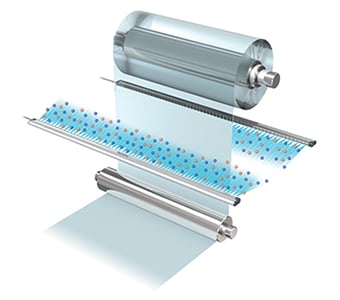
Case 1: Static elimination of films and sheets
Repeated contact and separation between film and roller causes significant buildup of static electricity. Static electricity can cause foreign particles to adhere to the films. Static elimination is essential as large static discharges can also lead to accidents.
An airless ionizer can remove static charge from thin sheets and films without making them flutter. Efficient delivery of ions to target objects can eliminate static electricity over a wide area even without the use of supplied air.
Case 2: Static elimination of tiny workpieces
Workpieces carried on a parts feeder can become charged through friction. Charged workpieces are lifted slightly due to static electricity, which causes tiny workpieces to fly away when blown on by a static eliminator blower.
Using an airless ionizer allows fine parts to be neutralised without being affected by air flow. While installation space may be an issue for static elimination of small workpieces, compact space-saving spot types can airlessly remove static charge.